Why Is Clay Used to Describe Minerals
Clay minerals in soils belong to phyllosilicates group of minerals which in turn belong to silicate minerals. Clay minerals are composed mainly of silica alumina and water but they may also contain appreciable quantities of iron alkalies and alkaline earths.
Kaolinite The Clay Mineral Kaolinite Information And Pictures
Ceramic is the word used to describe an earthenware product.
. Mixed-layer phyllosilicates or interstratified phyllosilicates can be built up by two or more different components. Bureau of Mines the average person consumes or uses 40000 pounds of minerals every year. Clay minerals occur in small particle sizes.
The clay mineralogy of a soil is the result of several factors interacting with the soil parent. Clay minerals share another characteristic besides particle size. The word Phyllon in the Greek means leaf and thus the silicate minerals having leaf or sheet-like structure with thickness considerably smaller than the other two dimensions are known as.
Structurally the clay minerals are composed of planes of. Why do soils have a CEC. Accumulation and losses of substance.
Introduction to Clay Minerals Soils. It also includes the study of the mineralogical composition and electrical properties of the clay particles. According to the US.
CLAY MINERALS IN SOILS. Identify additional properties that can be used to identify some minerals. Kaolin is the principal constituent in china clay.
Kaolin ball clay stoneware earthenware and fire clay are some of the most widespread examples. Is ceramic a mineral. The term can either mean a very small-sized particle or a silicate mineral with a sheetlike texture.
In fact clay minerals make up about 40 of the minerals in sedimentary rocks. Polytypism will only be mentioned when we describe relevant features of clay mineral structures. Up to 24 cash back Clay mineralogy is the science dealing with the structure of clay minerals on microscopic molecular and atomic scale.
Clay acidic water affects rocks and leaves behind clay minerals Explain the process by which soil horizons develop and why the number of horizons typically increases as the soil evolves. Clay As land is cultivated and soil is forming nutrients become available for plants as the active fraction or organic matter is consumed by organisms. Clay minerals are called secondary silicates because they are formed from the weathering of primary rock-forming minerals.
Clay is formed by the mechanical and chemical breakdown of rocks. Water is essential for clay mineral formation and most clay minerals are defined as hydrous alumino silicates. The clay minerals are of clay-grade phyllosilicates phyllosilicate minerals whose natural occurrence is confined to the clay-size particle fraction.
Formed by the decomposition of orthoclase feldspar eg. It is moist and compact in nature that enables it to be used for pottery and ceramics. African Pegmatite is a leading supplier and processor of an extensive variety of minerals including a full spectrum of clay products for the most demanding.
They are separated from sand gravel and silt due to the negative electrical load on the crystal edges and positive. Under the same conditions other mineral species such as. They form as low-temperature alteration products of igneous and high-temperature metamorphic minerals in the presence of liquid water.
Clay minerals are the function minerals of the earths close to floor environments. Silicate minerals make up about 90 of the rock-forming minerals of the earths crust. Kaolinite- also includes dickite and nacrite.
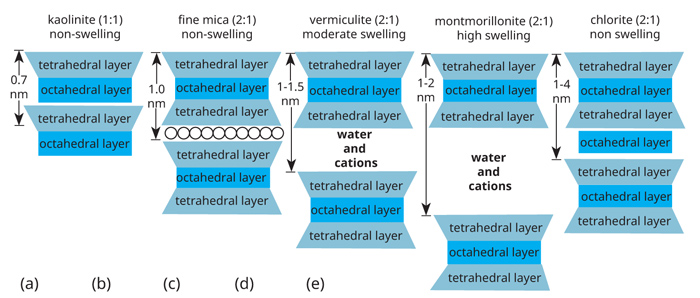
Each silicate clay particle is made up of individual layers or sheets. Clay minerals are always of small grain size. These are further separated into five groups that differ with respect to their net charge Table 2.
Clay minerals are layer silicates that are formed usually as products of chemical weathering of other silicate minerals at the earths surface. Clay minerals are an important group of minerals because they are among the most common products of chemical weathering and thus are the main constituents of the fine-grained sedimentary rocks called mudrocks including mudstones claystones and shales. Over the course of a lifetime an individual will use more than 1050 pounds of lead 1050 pounds of zinc 1750 pounds of copper.
The importance of minerals in everyday life is hardly recognized by the vast majority of people. They are found most often in shales the most common type of sedimentary rock. They shape in soils and sediments and through diagenetic and hydrothermal alteration of rocks.
If the mineral was pure silica and oxygen silica-. New York soils have silicate clay minerals clay minerals that contain silica. The most abundant silicates formed under the Earths normal surface conditions ie.
Further research on clay soil has shown that it contains elements that. Formed by the decomposition of some micas and feldspars. Unweathered rock exposed to physical and chemical weathering.
There are three main groups of clay minerals. Clay ceramics are a broad class of compounds with virtually limitless applications. Describe how color luster and streak are used to identify minerals.
Climate and consequent intensity of weathering. Earthenware pots bowls jugs ect is generally made from clay although there are other materials with. Within the soil profile often related to its position in the landscape.
Structures with more than two components are less common possibly because it is difficult to recognize. In cool dry or temperate climates clay minerals are fairly stable and are an important component of soil. The behavior of fine grained soils on the other hand depends to a large extent on the nature and characteristics of.
Illite- also includes glauconite a green clay sand and are the commonest clay minerals. Explain how the hardness of a mineral is measured. Hydrous silicate minerals known as clay minerals.
Soils have a CEC primarily because clay particles and organic matter in the soil tends to be negatively charged. Clay minerals are generally classified into three layer types based upon the number and arrangement of tetrahedral and octahedral sheets in their basic structure. Clay is high in terms of nutrients and minerals that are required for the growth of plants.

Clay Mineral Geology Definition Petroblogger Com
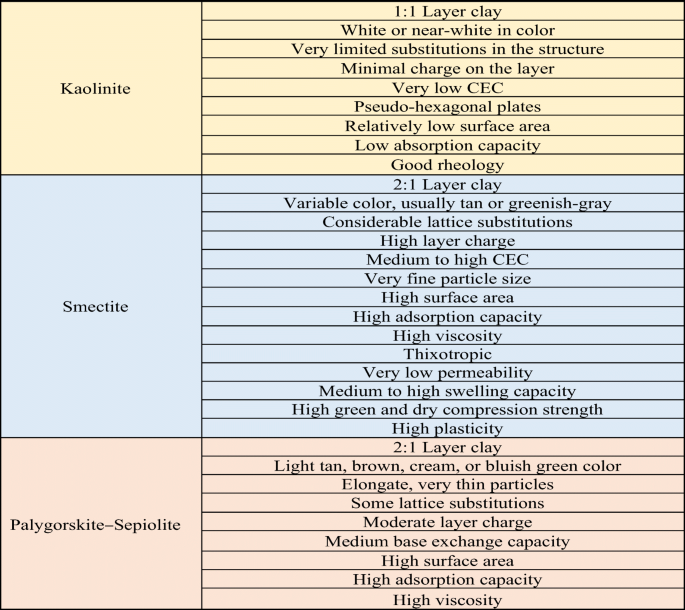
The Advantages Of Clay Mineral Modification Methods For Enhancing Adsorption Efficiency In Wastewater Treatment A Review Springerlink
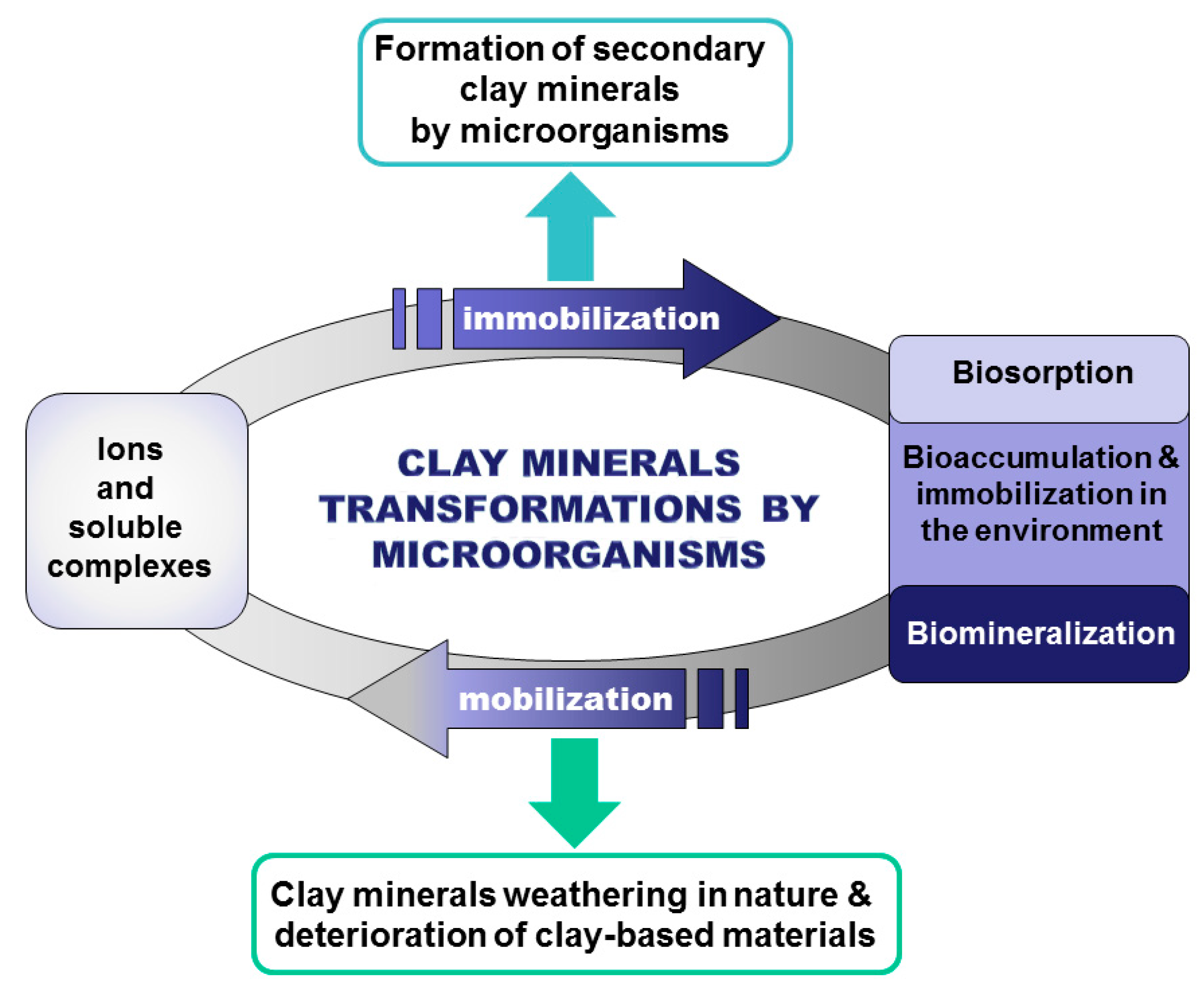
Minerals Free Full Text Microbial Interaction With Clay Minerals And Its Environmental And Biotechnological Implications Html

Clays Mineral Information Data And Localities
Clay Minerals Clays And Minerals

Structure Of 1 1 And 2 1 Clay Minerals Sivakugan 2001 Download Scientific Diagram
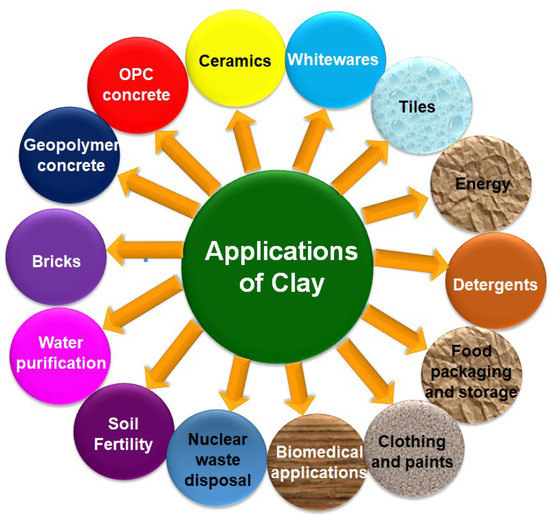
Industrial Application Of Clays And Clay Minerals

Clay Minerals Organic Matter Interactions In Relation To Carbon Stabilization In Soils Sciencedirect

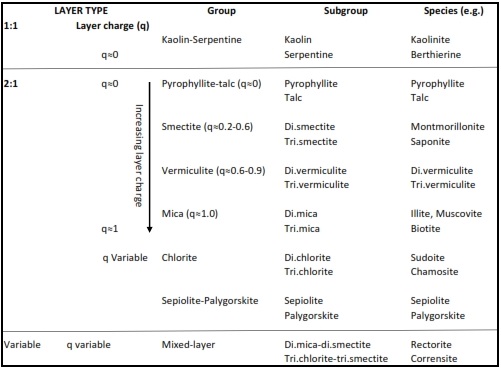
Classification Of Clay Minerals From Brindley 1952 Download Scientific Diagram

The Clay Minerals Society Educational Activities Smectite Minerals Education Coalition

Classification Of Clay Minerals From Brindley 1952 Download Scientific Diagram

Soil The Producer S Most Important Asset Part 4 The Clay Minerals

Major Groups Of Clay Minerals Download Table

Uses And Applications Of Clays And Clay Minerals State Of The Art And Perspectives Persee
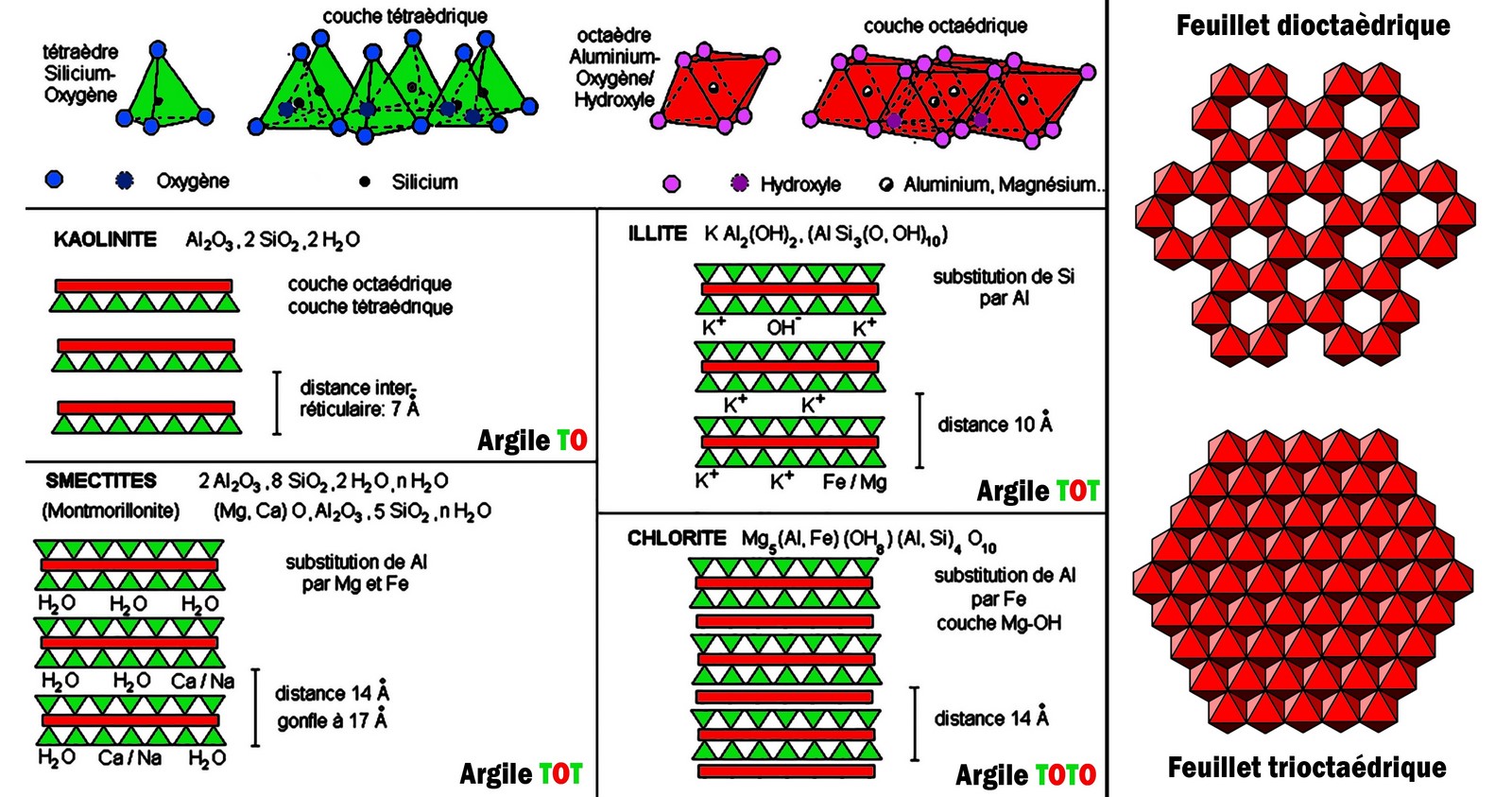




Comments
Post a Comment